Artículos
Pole vaulting is a wellknown sport requiring strength and coordination of complex movements over 4 general phases.
All phases involve a transfer of energy between the athlete and the pole to achieve the goal of clearing the crossbar. In track and field, jumping athletes have proven to be some of the most injury prone, with several studies finding common locations of pole vaulting injuries to be the thigh, ankle, and foot. Most reported injuries are mild and of muscular or ligamentous etiology. Stress fractures are also relatively common in athletes; however, fractures of the anterior tibial plafond and medial malleolus are rare.
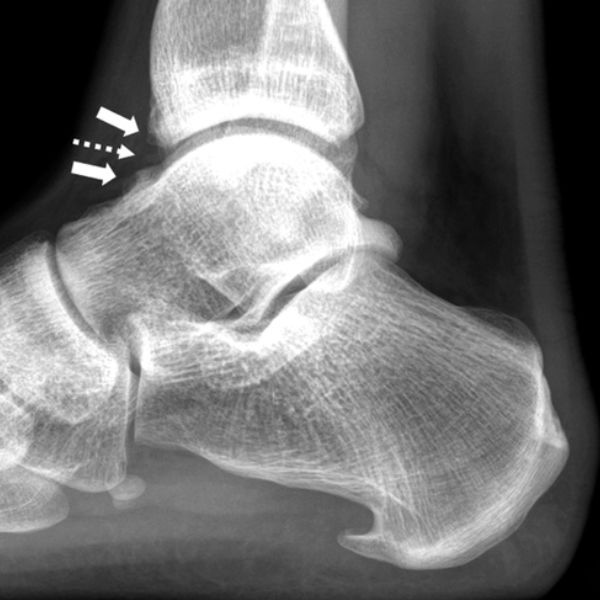
A longitudinally oriented tibial plafond fracture was first reported in a professional basketball player in 1990. To our knowledge, there have been no other cases of tibial plafond fractures reported since and none involving competitors in track and field jumping sports.
We present a case of a young male pole vaulter with a sports related tibial plafond stress fracture. This case adds to the few recorded incidents of stress fractures at the tibial plafond in athletes.
Although rare, it is important for healthcare providers to understand the factors contributing to this pathology and keep the diagnosis in mind when evaluating an athlete presenting with ankle or foot pain because delayed treatment increases the risk of future complications.
The patient was informed that data concerning the case would be submitted for publication, and he provided consent.
Suscríbete para conocer este caso y otros más dentro de nuestra revista semestral:
Más Artículos
Stephen Saela, MD, Michael Pompliano, MD, Jeffrey Varghese, MD, Kumar Sinha, MD, Michael Faloon, MD,
Arash Emami, MD. – 04/10/23
The literature on musculoskeletal tumors continues to be robust; however, it has been dominated by retrospective obser- vational studies. For bone sarcomas, cytotoxic chemotherapy remains the mainstay of systemic therapy, with no new, effective, targeted biologic interventions. There has been a renewed focus on functional outcomes and socioeconomic factors associated with oncologic outcomes and ongoing interest in pelvic reconstruction, which continues to have high rates of surgical complications.